Biology (from the Latin ‘bios’ meaning life and ‘logia’ meaning study of) is the study of all organisms and all aspects of their life-cycles.
Biology
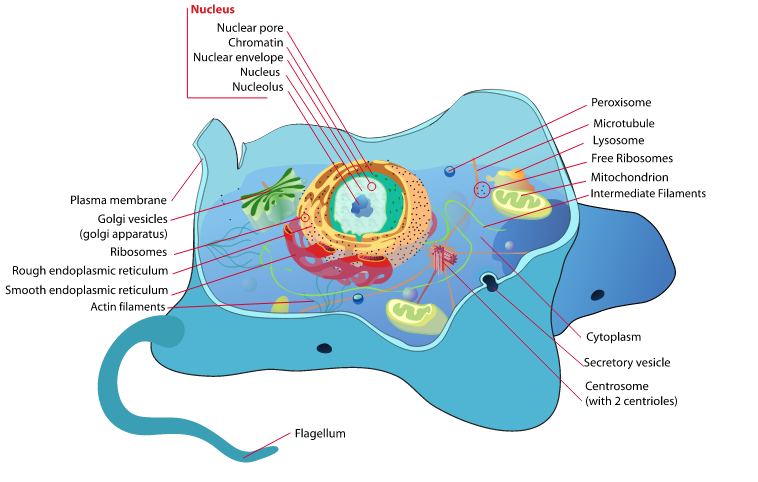
Biology (from the Latin ‘bios’ meaning life and ‘logia’ meaning study of) is the study of all organisms and all aspects of their life-cycles. The subject of Biology, as we know it today, was born in the nineteenth century along with physics, chemistry and the scientific method. Before then ‘Natural Philosophy’ which was the study of nature and the physical universe, included biology, chemistry and physics.
Natural Philosophy The study of our natural world is known to date back to the time of Mesopotamia around 3,100 BC but as this was the beginning of written historic record the study probably existed long before this time. Modern Biology The first great development of modern biology came from Charles Darwin, who is often referred to as the father of modern biology. Although known for his work ‘On the Origin of Species’ (published in 1859), Darwin produced nineteen additional publications, wrote hundreds of scientific papers and fourteen thousand letters, all of which laid the foundations for Biology as a subject we recognise today. Although he did not invent the theory of evolution, he certainly made the idea more accessible to the world. His theory was evolution by natural selection; where by an organism with a mutation may be better adapted to certain environmental changes and therefore improve their chance of survival. This means the organism with the useful mutation is more likely to survive, reproduce and hopefully pass on the useful mutation. Overtime species are able to adapt to the world around them and this process gave the Galapagos Islands (and the world) the rich diversity of its inhabitants. Deoxyribonucleic acid or DNA was first discovered in 1869 but its role was not known at the time. It was in 1943 that it was discovered that it is DNA that is responsible for programming the genetic makeup of organisms and passing on the mutations Darwin had discovered. This new understanding of how amino acids are programmed on a cellular level to make up various parts of the organism was a huge leap forward but new profound discoveries are being made everyday in the field of biology.
Discovering the Fascinating World of Xenarthra: The Slow-Moving Sloths, Armoured Armadillos and Unique True Anteaters
Xenarthra is a diverse group of mammals that includes sloths, armadillos, and anteaters. The name “Xenarthra” comes from the Greek words “xenos” meaning strange or different, and “arthron” meaning joint. This name reflects the unique skeletal structure found in these animals, particularly in their vertebrae and pelvic bones. Within the Xenarthra group, there are several different species, each with its own unique characteristics and adaptations. Sloths are known for their slow-moving nature and their ability to hang upside down from trees. Armadillos are known for their armored shells and ability to roll into a ball for protection. Anteaters are known for their long snouts and tongues, which they use to feed on ants and termites. Despite their differences, all Xenarthra species share a common ancestor and are found primarily in the Americas. Summary Xenarthra is a diverse group of mammals found in South and North America. Sloths are slow-moving but highly adapted to life in the canopy. Armadillos are survivors from prehistoric times and have unique armour for protection. True anteaters are specialized insectivores with long snouts and tongues. Xenarthra face threats and conservation efforts are needed to protect them. Slow-Moving Sloths: Masters of Adaptation in the Canopy Sloths are perhaps the most well-known members of the Xenarthra group. They are known for their slow movements and spend most of their lives hanging upside down from trees. This slow lifestyle is due to their low metabolic rate, which allows them to conserve energy. Sloths have several physical adaptations that make them well-suited for life in the trees. They have long limbs with curved claws that allow them to easily...
A Fascinating Look into the World of Tubulidentata: The Enigmatic Aardvarks
Tubulidentata is a small and enigmatic order of mammals that consists of only one living species, the aardvark (Orycteropus afer). Aardvarks are unique creatures that have captured the curiosity of scientists and researchers for centuries. They are native to Africa and are known for their distinctive appearance and unusual habits. Studying aardvarks is not only fascinating but also important for understanding the evolution of mammals. Summary Tubulidentata is a mysterious order of aardvarks that has unique features that make them stand out. Aardvarks have evolved over time and have a unique anatomy that makes them stand out from other animals. Aardvarks are found in the wild in specific habitats and have unique behavioural patterns. Aardvarks have an unusual diet that defies classification and have unique reproductive and social behaviours. Aardvarks are significant in African folklore and mythology, but they face conservation challenges that require efforts to protect them. Evolutionary Origins of Aardvarks: A Journey through Time The fossil record of aardvarks and their ancestors provides valuable insights into their evolutionary origins. Fossils dating back millions of years have been discovered in various parts of Africa, revealing the gradual development of the aardvark’s unique adaptations. These adaptations allowed them to survive and thrive in their environment. One of the most notable features of aardvarks is their long snouts, which are perfectly designed for their diet and lifestyle. Their snouts are equipped with powerful claws that enable them to dig burrows and search for food. These adaptations have been refined over millions of years, making aardvarks highly efficient in their daily activities. Anatomy of Aardvarks: Unique Features that Make Them...
Sirenia: The Gentle Giants of the Sea – A Fascinating Insight into Dugongs and Manatees
Sirenia, also known as sea cows, are a group of large marine mammals that belong to the order Sirenia. They are characterized by their large size, herbivorous diet, and gentle nature. The two main species of Sirenia are the dugongs and manatees. Dugongs are found in the warm coastal waters of the Indian and Pacific Oceans, while manatees are found in the warm coastal waters of the Atlantic Ocean and the Gulf of Mexico. Summary Sirenia are gentle giants of the sea, including dugongs and manatees. Dugongs and manatees have unique anatomy and physiology, adapted for their aquatic lifestyle. Sirenia have a long evolutionary history, dating back millions of years. Dugongs and manatees are found in specific habitats and have distinct feeding habits. The reproduction and life cycle of Sirenia are fascinating and complex. The Anatomy and Physiology of Dugongs and Manatees Sirenia have a number of physical characteristics that make them well-suited for life in the water. They have streamlined bodies, with a large, rounded head and a tapering tail. Their bodies are covered in a thick layer of blubber, which helps to insulate them from the cold water. They also have paddle-like flippers, which they use to swim through the water. In addition to their physical adaptations, Sirenia also have a number of physiological adaptations that allow them to live in an aquatic environment. For example, they have lungs that are adapted for holding their breath underwater. They can stay submerged for up to 20 minutes before needing to come up for air. They also have a specialized digestive system that allows them to extract nutrients from...
Exploring the Fascinating World of Scandentia: The Tree Shrews of Britain
Tree shrews, scientifically known as Scandentia, are small mammals that belong to the order Scandentia. Despite their name, tree shrews are not actually shrews, but rather a distinct group of animals that share some characteristics with both primates and rodents. They are found in various parts of the world, including Britain, where they play an important role in the local ecosystems. Tree shrews are small, agile creatures that are well adapted for life in the trees. They have a slender body with a long tail that helps them maintain balance while climbing. Their limbs are also well suited for arboreal life, with long fingers and toes that allow them to grip branches and move quickly through the trees. Tree shrews have a pointed snout and large eyes, which give them excellent vision and help them locate food and avoid predators. In British ecosystems, tree shrews play a crucial role in maintaining the balance of the ecosystem. They are important seed dispersers, as they eat fruits and then excrete the seeds in different locations. This helps to spread plant species and promote biodiversity. Tree shrews also serve as prey for larger predators, such as owls and snakes, helping to regulate their populations. Overall, tree shrews are an integral part of the British ecosystem and their presence is vital for its health and stability. Summary Scandentia, also known as tree shrews, are small mammals found in Britain. Tree shrews are classified as their own order, separate from rodents and primates. Tree shrews have sharp claws and long tails, and are active during the day. Tree shrews are found in forests and...
The Fascinating World of Rodentia: Exploring the Diversity of Squirrels, Chipmunks, Rats, Mice, Voles, Beavers and Lemmings in the UK
Rodents are a diverse group of mammals that belong to the order Rodentia. They are characterized by their continuously growing incisors, which they use for gnawing and chewing. With over 2,000 species worldwide, rodents make up the largest group of mammals on Earth. They can be found in almost every habitat, from deserts to forests, and from grasslands to urban areas. One of the key characteristics of rodents is their ability to adapt and thrive in various environments. They have a wide range of body sizes, from tiny mice to large beavers, and they exhibit a variety of behaviors and feeding habits. Rodents play a crucial role in ecosystems as both prey and predators, and their presence is essential for maintaining the balance of nature. Summary Rodents are a diverse family of mammals that includes squirrels, chipmunks, rats, mice, voles, beavers, and lemmings. Squirrels are the most common and beloved rodent in the UK, while chipmunks are a lesser-known but adorable species. Rats and mice are pests that invade our homes and cities, while voles are tiny creatures with a big impact on ecosystems. Beavers are large and powerful rodents that shape our rivers, and lemmings are mysterious and misunderstood creatures of the Arctic. Rodents play a vital role in the UK ecosystem as a link in the food chain, and conservation efforts are necessary to protect endangered species and manage populations. Squirrels: The Most Common and Beloved Rodent in the UK Squirrels are perhaps the most well-known and beloved rodents in the UK. There are two main types of squirrels found in the country: the native red squirrel...
The Majestic Proboscidea: Exploring the Fascinating World of Elephants
Elephants are one of the most iconic and majestic creatures on Earth. They have a long and rich history, dating back millions of years. These gentle giants belong to the family Elephantidae and are the largest land animals on the planet. There are three main species of elephants: the African bush elephant, the African forest elephant, and the Asian elephant. Elephants have a distinctive appearance with their large bodies, long trunks, and tusks. They can weigh up to several tons and stand at an impressive height of 10 to 13 feet at the shoulder. Their trunks are versatile appendages that serve multiple functions, including breathing, smelling, drinking, and grasping objects. Elephants also have large ears that help regulate their body temperature. Summary Elephants are majestic creatures with unique features and remarkable cognitive abilities. They have complex social structures and communication methods that are still being studied. The evolutionary history of elephants can be traced back millions of years to the Proboscidea family. Elephants play a crucial role in shaping their environment and maintaining ecosystem balance. Unfortunately, human activities pose a significant threat to elephant populations, but conservation efforts are underway to protect them. Understanding Elephant Behaviour: From Social Structures to Communication Elephants are highly social animals that live in complex family groups known as herds. These herds are led by a matriarch, usually the oldest and most experienced female in the group. The matriarch is responsible for making decisions and guiding the herd to food and water sources. Communication is vital for elephants to maintain social cohesion within their herds. They use a variety of methods to communicate with...
Exploring the Fascinating World of Primates: From Lemurs to Humans
Primates are a diverse group of mammals that includes humans, apes, monkeys, and prosimians such as lemurs and tarsiers. They are characterized by their forward-facing eyes, grasping hands and feet, and complex social behaviors. Primates can be found in a variety of habitats around the world, from tropical rainforests to savannahs and even high-altitude mountain ranges. The diversity of primates is vast, with over 500 species identified to date. They vary greatly in size, ranging from the tiny pygmy mouse lemur, which weighs just 30 grams, to the large male gorilla, which can weigh up to 200 kilograms. Primates also exhibit a wide range of adaptations to their environments. For example, lemurs have long tails that they use for balance when leaping through the trees, while spider monkeys have long limbs that allow them to swing effortlessly from branch to branch. Summary Primates are a diverse group of animals with unique adaptations to their environments. The evolutionary history of primates spans from ancient prosimians to modern humans. Primates have unique anatomical and physiological features, such as opposable thumbs and binocular vision. Primate social structures and communication are complex and varied. Primate intelligence and cognition are demonstrated through learning, memory, and problem-solving. Evolutionary History of Primates: From Ancient Prosimians to Modern Humans The evolutionary history of primates stretches back over 60 million years. The earliest primates were small, nocturnal animals that resembled modern-day lemurs and tarsiers. These early primates lived in trees and had adaptations such as grasping hands and feet for climbing and leaping. Over time, primates evolved into two main groups: the prosimians and the anthropoids. Prosimians include...
Pholidota: The Fascinating World of Britain’s Spiny Anteaters
Pholidota, commonly known as pangolins or spiny anteaters, are a unique group of mammals that belong to the order Pholidota. They are characterized by their distinctive scales, which cover their bodies and provide them with protection against predators. Pholidota are fascinating creatures that have captured the attention of scientists and researchers around the world, including those in Britain. Studying Pholidota in Britain is of great importance for several reasons. Firstly, it allows us to gain a better understanding of the biodiversity and ecological dynamics of the country. Pholidota play a crucial role in maintaining the balance of ecosystems by controlling populations of ants and termites, which are their primary food sources. Additionally, studying Pholidota in Britain helps us to assess the health of their populations and the impact of human activities on their habitats. Summary Pholidota, also known as spiny anteaters, are native to Britain and have unique physical characteristics such as scales and long tails. They are solitary and nocturnal creatures that feed on ants, termites, and other insects. Pholidota’s habitat and distribution in Britain are threatened by habitat loss and hunting. Conservation efforts are being made to protect Pholidota and their importance in the ecosystem cannot be overstated. The future of Pholidota in Britain faces challenges, but opportunities for their protection and preservation exist. The Physical Characteristics of Pholidota: From Scales to Tails Pholidota are easily recognizable by their unique physical features. They have a cylindrical body covered in overlapping scales made of keratin, similar to those found in human hair and nails. These scales provide them with protection against predators and are one of the defining...
Exploring the Fascinating World of Perissodactyla: A Closer Look at Horses, Rhinos, Tapirs and Zebras
Perissodactyla is a group of mammals that includes horses, rhinos, and tapirs. The name Perissodactyla comes from the Greek words “perissos,” meaning odd or uneven, and “daktylos,” meaning finger or toe. This refers to the uneven number of toes on their feet, with horses having one toe and rhinos and tapirs having three toes. Perissodactyla is an important group in the animal kingdom due to their unique characteristics and ecological roles. They are herbivores, which means they play a crucial role in maintaining the balance of plant populations in their habitats. Additionally, they have fascinating adaptations that have allowed them to survive and thrive in various environments. One fascinating fact about Perissodactyla is their size. Some species, such as the African elephant, can reach heights of up to 13 feet and weigh over 7,000 pounds. This makes them some of the largest land animals on Earth. Another interesting fact is their ability to run at high speeds. Horses, for example, can reach speeds of up to 55 miles per hour, making them one of the fastest land animals. Summary Perissodactyla are a fascinating group of animals that includes horses, rhinos, tapirs, and zebras. Understanding the unique anatomy of horses can help us appreciate their beauty and athleticism. Rhinos have evolved over millions of years and are now endangered due to human activity. Tapirs are elusive creatures with interesting habits and characteristics. The science behind zebra stripes is still being studied, but they are thought to serve as camouflage and a way to deter biting insects. Horse Anatomy: Understanding the Unique Features of These Magnificent Creatures Horses have a unique...
Exploring the Fascinating World of Peramelemorphia: A Closer Look at the Curious Bandicoots
Peramelemorphia is an order of marsupials that includes the bandicoots, a group of small to medium-sized mammals found in Australia and New Guinea. These unique creatures have captured the attention of scientists and nature enthusiasts alike due to their fascinating characteristics and behaviors. Studying Peramelemorphia is important for understanding the diversity of marsupials and their role in ecosystems. Bandicoots are known for their distinctive physical features, such as their long snouts, sharp claws, and rabbit-like hind legs. They have adapted to a wide range of habitats, from forests to grasslands, and have unique feeding habits and reproductive strategies. These traits make them an intriguing subject for research and conservation efforts. Summary Peramelemorphia are a fascinating group of marsupials found in Australia and New Guinea. Bandicoots, a type of Peramelemorphia, have a long evolutionary history dating back to the early Miocene period. Bandicoots have unique physical characteristics such as a pointed snout and powerful hind legs for digging. Bandicoots can be found in a variety of habitats across Australia and New Guinea, including forests, grasslands, and deserts. Bandicoots are nocturnal and solitary animals that feed on a variety of insects, small animals, and plant matter. The History of Bandicoots: Origins and Evolution of Peramelemorphia. The evolutionary history of Peramelemorphia dates back millions of years. Fossil records show that bandicoot-like animals have existed since the early Miocene epoch, around 20 million years ago. These early ancestors were small, insectivorous mammals that lived in rainforests. Over time, bandicoots evolved to occupy a variety of ecological niches. Some species became specialized diggers, using their strong forelimbs and sharp claws to excavate burrows and...
Exploring the Fascinating World of Paucituberculata: Britain’s Shrew Opossums
Shrew opossums, belonging to the order Paucituberculata, are a group of small marsupials that are native to South America. However, what many people may not know is that there is a species of shrew opossum that can be found in Britain. These fascinating creatures are known for their unique physical characteristics and interesting behavioural patterns. In this article, we will explore the taxonomy, physical characteristics, habitat and distribution, behavioural patterns, feeding habits, reproduction and life cycle, threats and conservation status, importance in ecosystems, and future research and conservation efforts of shrew opossums in Britain. Summary Paucituberculata are shrew opossums found in Britain. Shrew opossums are classified as marsupials and are closely related to kangaroos and koalas. Shrew opossums have a small body size, pointed snouts, and prehensile tails. Shrew opossums are found in the Andes Mountains and have not been observed in Britain since the Pleistocene era. Shrew opossums are solitary and nocturnal animals that feed on insects, small mammals, and fruits. Taxonomy and Classification of Paucituberculata Shrew opossums belong to the order Paucituberculata, which is a small group of marsupials that is only found in South America. They are further classified into the family Caenolestidae, which consists of four genera: Caenolestes, Lestoros, Rhyncholestes, and Caenolestoides. The shrew opossum species found in Britain is known as the British shrew opossum (Caenolestes britannicus). This species was first discovered in the early 20th century and has since been the subject of much scientific interest. Physical Characteristics of Shrew Opossums Shrew opossums are small mammals, typically measuring around 10-15 centimeters in length. They have a slender body with short legs and a...
Notoryctemorphia: The Fascinating World of Marsupial Moles in Australia
Notoryctemorphia is an order of marsupial moles that is unique to Australia. These small, burrowing mammals are known for their cylindrical body shape, lack of external ears and eyes, and specialized digging claws. They are classified as an order within the marsupial infraclass, which also includes kangaroos, koalas, and wombats. Studying marsupial moles is important for understanding the diversity of Australian fauna. Australia is home to a wide range of unique and endemic species, and marsupial moles are no exception. By studying these fascinating creatures, scientists can gain insights into the evolutionary history and adaptations of Australian mammals. Summary Notoryctemorphia is a unique order of marsupial moles found only in Australia. Marsupial moles have physical adaptations such as a streamlined body and shovel-like forelimbs for life underground. Marsupial moles are found in arid and semi-arid regions of Australia and are threatened by habitat loss and fragmentation. Marsupial moles feed on insects and have a unique reproductive system where females have only two teats. The evolutionary history of marsupial moles in Australia dates back to the Miocene epoch and they are considered a living fossil. The Physical Characteristics of Marsupial Moles: Adaptations for Life Underground Marsupial moles have several unique physical features that allow them to thrive in their underground habitat. Their cylindrical body shape is ideal for moving through the soil, as it reduces resistance and allows them to navigate narrow tunnels. They lack external ears and eyes, as these features are unnecessary in their dark underground environment. One of the most striking adaptations of marsupial moles is their specialized digging claws. These claws are long and curved, allowing...








