Angola
(República de Angola (Republic of Angola))
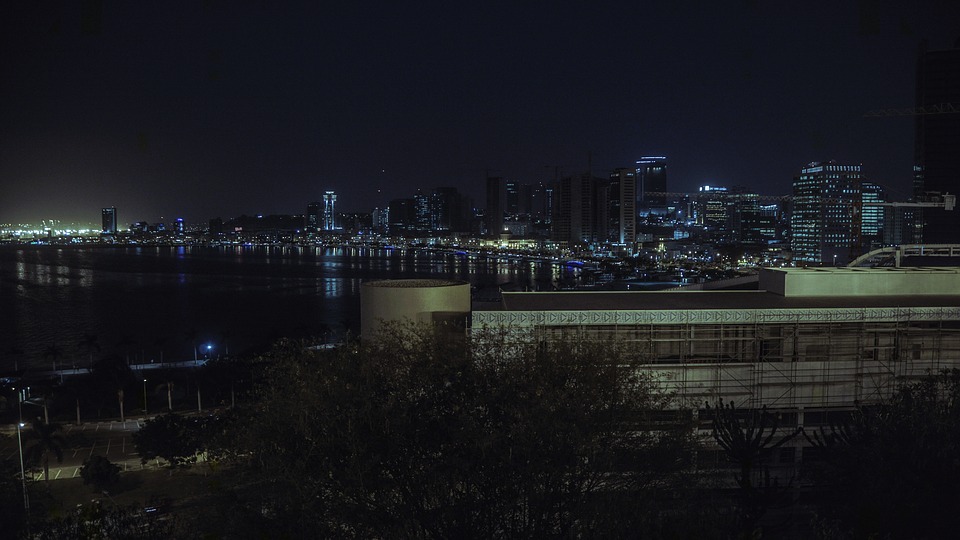

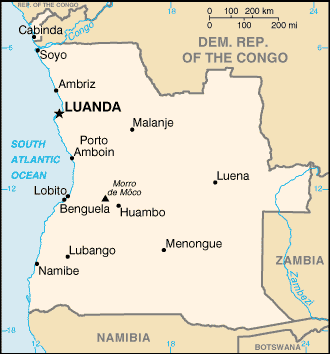




Capital: Luanda
Population (Estimated July 2012): 18,056,072
Area: 1,246,700km2 or 481,354 mi2
Currency: Kwanza (AOA)
Official Language: Portuguese
Political Information: Multiparty Presidential Republic
Official Religion: No Official Religion (approximately 47% of the population have indigenous religious beliefs, 38% are Roman Catholic and 15% are Protestant)
Highest Mountain: Mount Mocco (Morro de Moco) at 2,620m or 8596
GDP Official Exchange Rate (OER is more precise at gauging a countries economic power)
(Estimated 2011): $99.3 billion (US$) or £59,580 million(GBP)
GDP (OER) Per Capita (per member of the population estimated 2011): (US$) or (GBP)
GDP Purchasing Power Parity (PPP is good for gauging living conditions and use of resources but not as accurate as OER. This data has been calculated based on the sum value of all goods and services produced in the country valued at prices prevailing in the United States)
(Estimated 2011): $115.9 billion (US$) or £69,540 million(GBP)
GDP (PPP) Per Capita (per member of the population estimated 2011): $5,900 (US$) or £3,540(GBP)
Time Zone (GMT/UTC): +1:00
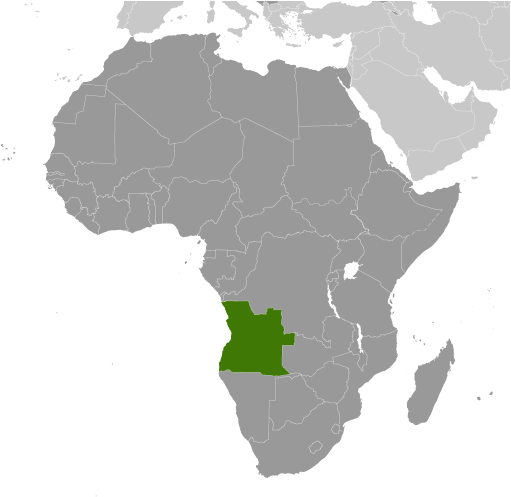
Counties/Provinces/States: Provinces (provincias, singular – provincia); Bengo, Benguela, Bie, Cabinda, Kwando Kubango, Kwanza Norte, Kwanza Sul, Cunene, Huambo, Huila, Luanda, Lunda Norte, Lunda Sul, Malanje, Moxico, Namibe, Uige, Zaire
Leaders: President Jose Eduardo Dos Santos; Vice President Fernando “Nando” da Piedade Dias Dos Santos
Sources: CIA World Fact Book, Encyclopaedia Britannica,
Angola, officially known as the Republic of Angola, is a country located in Southern Africa. It is bordered by Namibia to the south, Zambia to the east, and the Democratic Republic of the Congo to the north. With a population of over 30 million people, Angola is one of the largest countries in Africa. The capital city of Angola is Luanda.
Angola holds great importance in Africa due to its rich natural resources, including oil, diamonds, and minerals. It is one of the largest oil producers in Africa and has a significant impact on the global oil market. The country’s economy heavily relies on its natural resources, making it an important player in the African continent.
Angola’s History: From Colonialism to Independence
Angola has a complex history that dates back to the era of colonialism. The Portuguese arrived in Angola in the 15th century and established a colony that lasted for over four centuries. During this time, Angola became a major hub for the transatlantic slave trade, with millions of Africans being forcibly taken from the country.
The struggle for independence began in the 1950s when nationalist movements emerged, demanding an end to Portuguese rule. The most prominent of these movements was the Popular Movement for the Liberation of Angola (MPLA), led by Agostinho Neto. After years of armed conflict and international pressure, Angola finally gained independence from Portugal on November 11, 1975.
However, independence did not bring stability to Angola. Instead, it plunged into a devastating civil war that lasted for nearly three decades. The civil war was fought between three main factions: the MPLA, the National Union for the Total Independence of Angola (UNITA), and the National Front for the Liberation of Angola (FNLA). The war resulted in immense suffering for the Angolan people, with millions displaced and thousands killed.
Angola’s Geography: A Diverse Landscape
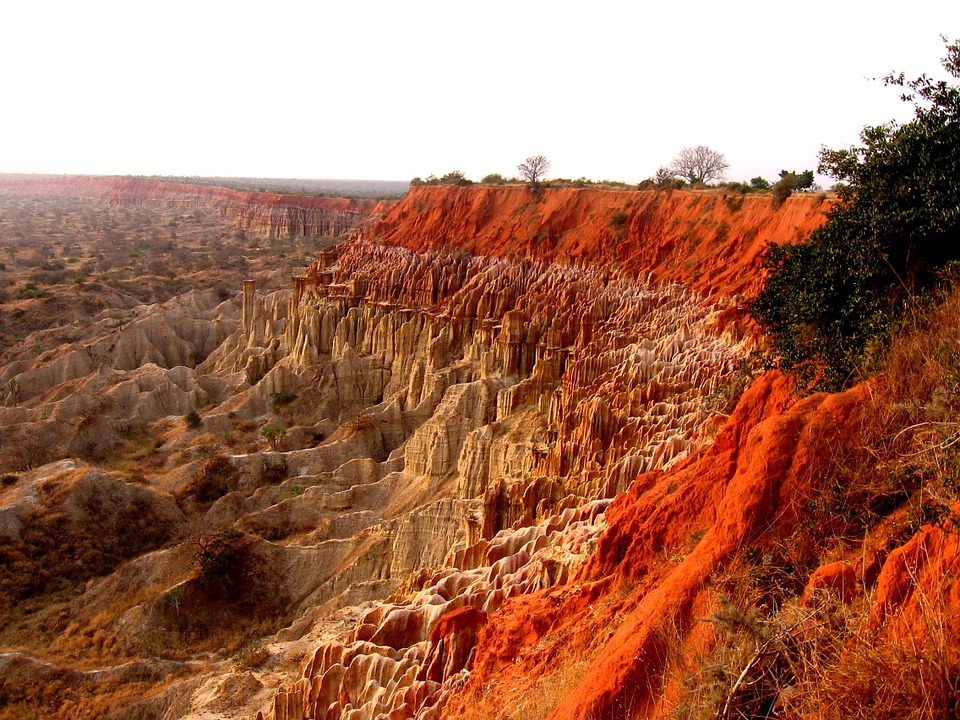
Angola is a country with a diverse and varied landscape. It is characterized by four main regions: the coastal plain, the central plateau, the highlands, and the eastern lowlands. The coastal plain stretches along the Atlantic Ocean and is home to major cities such as Luanda and Benguela.
The central plateau is the most populous region of Angola and is known for its fertile soil. It is an important agricultural area, producing crops such as maize, cassava, and beans. The highlands, located in the central part of the country, are known for their stunning landscapes and cooler climate. They are also rich in minerals such as diamonds and copper.
The eastern lowlands, also known as the Zambezi Basin, are characterized by vast grasslands and savannahs. This region is home to a diverse range of wildlife, including elephants, lions, and giraffes. Angola’s geography also includes several major rivers, such as the Cuanza, Kwanza, and Zambezi, which play a crucial role in the country’s agriculture and transportation.
Angola’s People: Ethnic Diversity and Culture
Angola is a country with a rich ethnic diversity, with over 90 different ethnic groups. The largest ethnic group in Angola is the Ovimbundu, followed by the Mbundu and the Bakongo. Each ethnic group has its own distinct culture, traditions, and languages.
Angolan culture is deeply rooted in African traditions and customs. Music and dance play a significant role in Angolan culture, with various traditional dances such as kizomba, semba, and kuduro being popular throughout the country. These dances are often accompanied by traditional instruments such as drums and marimbas.
Angola’s cultural heritage also includes traditional crafts such as pottery, weaving, and wood carving. These crafts are not only a means of artistic expression but also an important source of income for many Angolans. The country’s rich cultural heritage is celebrated through various festivals and events, such as the Luanda International Jazz Festival and the National Festival of Angolan Culture.
Angola’s Economy: A Resource-Rich Nation
Angola is a resource-rich nation, with its economy heavily reliant on its natural resources. The country is one of the largest oil producers in Africa, with oil accounting for the majority of its export revenue. Angola is also rich in diamonds, minerals, and agricultural resources.
The oil industry plays a crucial role in Angola’s economy, contributing to over 90% of its export earnings. However, the country’s heavy reliance on oil makes it vulnerable to fluctuations in global oil prices. In recent years, Angola has made efforts to diversify its economy by investing in sectors such as agriculture, manufacturing, and tourism.
Despite its vast natural resources, Angola faces several challenges in its economy. One of the major challenges is the high level of corruption, which hinders economic development and discourages foreign investment. Additionally, the country’s infrastructure is in need of significant improvement, particularly in areas such as transportation and energy.
Angola’s Politics: A Struggle for Democracy
Angola has a complex political history that has been marked by decades of authoritarian rule and a struggle for democracy. After gaining independence from Portugal in 1975, Angola was ruled by the MPLA under President Agostinho Neto. However, the country soon descended into a civil war between the MPLA and UNITA.
The civil war ended in 2002 with the death of UNITA leader Jonas Savimbi. Since then, Angola has made progress towards democracy, holding several elections and transitioning to a multi-party system. However, there are still concerns about the lack of political freedom and human rights abuses in the country.
The current president of Angola is João Lourenço, who took office in 2017. Lourenço has made efforts to combat corruption and improve governance in the country. However, there is still a long way to go in terms of achieving true democracy and ensuring the protection of human rights in Angola.
Angola’s Education: Challenges and Opportunities
Angola’s education system faces several challenges, including a lack of infrastructure, qualified teachers, and resources. The country has made progress in recent years in expanding access to education, with an increase in enrollment rates at the primary and secondary levels. However, there is still a significant disparity in access to education between urban and rural areas.
One of the major challenges in Angola’s education system is the high dropout rate, particularly at the secondary level. Many students are forced to drop out of school due to poverty, lack of transportation, and the need to work to support their families. Additionally, there is a shortage of qualified teachers, particularly in rural areas.
Despite these challenges, there are opportunities for improvement in Angola’s education system. The government has recognized the importance of education in driving economic development and has made efforts to invest in the sector. There are also several non-governmental organizations and international partners working to improve access to quality education in Angola.
Angola’s Healthcare: Progress and Challenges
Angola’s healthcare system has made significant progress in recent years but still faces several challenges. The country has made efforts to improve access to healthcare services, particularly in rural areas. The government has invested in building new healthcare facilities and training healthcare professionals.
However, there are still significant challenges in Angola’s healthcare system. One of the major challenges is the high prevalence of infectious diseases such as malaria, HIV/AIDS, and tuberculosis. These diseases put a strain on the healthcare system and require ongoing investment in prevention and treatment.
Another challenge is the lack of healthcare infrastructure and resources. Many healthcare facilities in Angola lack basic equipment and supplies, making it difficult to provide quality care. Additionally, there is a shortage of healthcare professionals, particularly in rural areas.
Angola’s Tourism: A Growing Industry
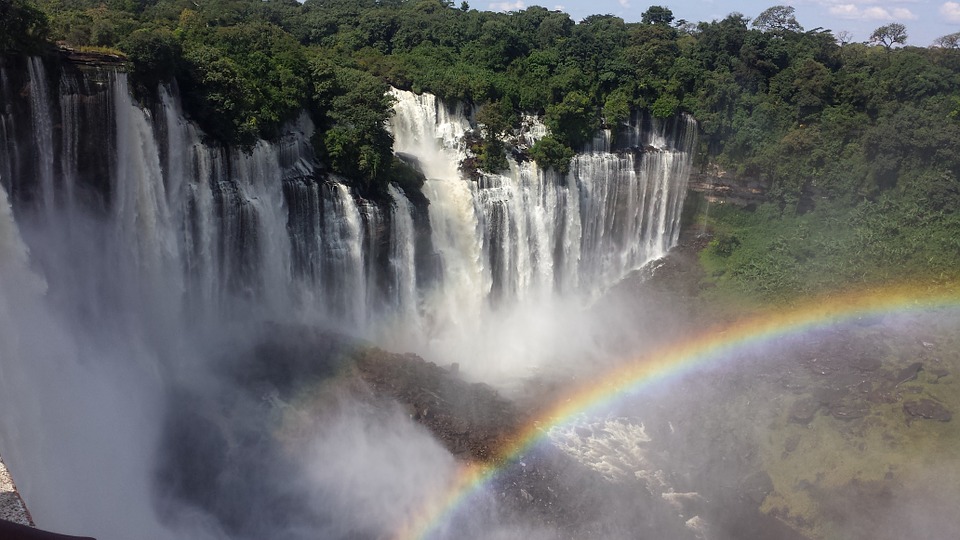
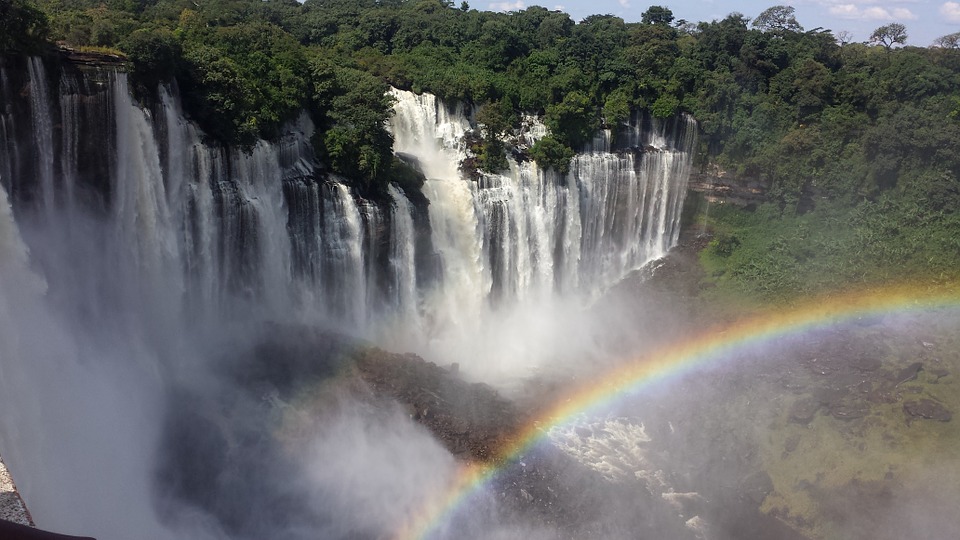
Angola’s tourism industry has great potential for growth, thanks to its diverse natural landscapes and cultural heritage. The country offers a range of tourist attractions, including stunning beaches, national parks, historical sites, and vibrant cities.
One of the main tourist attractions in Angola is the city of Luanda, with its beautiful coastline and vibrant nightlife. The city is known for its colonial architecture, such as the Fortress of São Miguel and the Palácio de Ferro. Other popular destinations include the Kissama National Park, which is home to a wide variety of wildlife, and the Tundavala Fissure, a breathtaking natural wonder.
Despite its potential, the tourism industry in Angola faces several challenges. One of the main challenges is the lack of infrastructure and services for tourists. There is a need for investment in hotels, transportation, and tourist facilities to attract more visitors.
Angola’s Future: Prospects and Challenges Ahead
The future of Angola holds both prospects and challenges. The country has made progress in recent years in terms of economic development, political stability, and social progress. However, there are still significant challenges that need to be addressed.
One of the main challenges is reducing poverty and inequality in Angola. Despite its vast natural resources, a large portion of the population still lives in poverty. There is a need for inclusive economic growth that benefits all segments of society.
Another challenge is improving governance and combating corruption. Corruption remains a major issue in Angola and hinders economic development and social progress. Efforts to strengthen institutions and promote transparency are crucial for the country’s future.
In conclusion, Angola is a country with a rich history, diverse geography, and vibrant culture. It holds great importance in Africa due to its natural resources and economic potential. While the country has made progress in recent years, there are still significant challenges that need to be addressed in order to ensure a bright future for Angola.
If you’re interested in learning more about Angola and its rich cultural heritage, you should definitely check out this fascinating article on “The Traditional Music of Angola” from the Array magazine. This insightful piece delves into the diverse musical traditions of Angola, exploring the rhythms, instruments, and styles that have shaped the country’s vibrant music scene. From the soulful melodies of semba to the energetic beats of kuduro, this article offers a captivating glimpse into the musical tapestry of Angola. So why not click here to read more and embark on a musical journey through Angola’s captivating soundscape?
Republic of Angola: Natural Resources, Diamond, Mineral Resources and Mining Industry
Republic of Angola: Natural Resources, Diamond, Mineral Resources and Mining Industry Angola, officially known as the Republic of Angola, is a nation rich in natural resources, boasting vast reserves of oil, diamonds, and various minerals. This abundance has positioned Angola as a significant player in the global mining industry. Understanding the natural resources of Angola is crucial for comprehending its economic landscape and the challenges and opportunities that come with resource wealth. Outline What Are Angola’s Primary Natural Resources? How Has Diamond Mining Shaped Angola’s Economy? The Role of Oil in Angola’s Economic Development Exploring Angola’s Iron Ore Reserves The Impact of Natural Resources on the Angolan Economy Challenges in Angola’s Mining Industry The Influence of Portuguese Colonisation on Resource Extraction Post-Civil War Recovery and Resource Management Angola’s Position in Sub-Saharan Africa‘s Resource Landscape Future Prospects for Angola’s Natural Resource Sector 1. What Are Angola’s Primary Natural Resources? Angola is endowed with a variety of natural resources, including petroleum, diamonds, iron ore, phosphates, copper, feldspar, gold, bauxite, and uranium. These resources have been central to the country’s economic activities and export revenues. The petroleum sector is particularly significant, contributing a substantial portion to Angola’s GDP and government revenue. Diamonds also play a crucial role, with Angola being one of the largest producers of diamonds in Africa. The mining of iron ore and other minerals further diversifies the country’s resource base. 2. How Has Diamond Mining Shaped Angola’s Economy? Diamond mining has been a cornerstone of Angola’s economy, especially since the end of the civil war. The country is among the top producers of diamonds globally, with significant...
Political Boundaries of Angola: Provinces, Districts, or Historical Boundaries.
Angola, located in Southern Africa, is a country with rich history and diverse cultures. Understanding Angola’s political boundaries is crucial for comprehending its governance, history, and the challenges faced by its people. Angola shares borders with several countries, including Namibia, Zambia, the Democratic Republic of Congo, and the Republic of Congo. The Atlantic Ocean forms Angola’s western boundary. These political boundaries have played a significant role in shaping Angola’s history and present-day circumstances. Summary Angola’s political boundaries have evolved over time, with the country currently divided into 18 provinces and 164 municipalities. The provincial divisions have historical and cultural significance, with some dating back to the colonial era and others established after independence. Districts are the smallest administrative units in Angola, responsible for providing basic services and governance to local communities. Angola’s historical boundaries have been shaped by colonialism, civil war, and international disputes, with some areas still contested today. The impact of Angola’s political boundaries on its people can be seen in issues such as access to resources, ethnic tensions, and regional disparities in development. Angola’s Provincial Divisions: History and Significance Angola is divided into 18 provinces, each with its own unique characteristics and cultural heritage. The provincial divisions in Angola have a long historical background that dates back to the colonial era. During the Portuguese colonial rule, Angola was divided into three major regions: Angola, Benguela, and Mozambique. These regions were further divided into districts and municipalities. The significance of provincial divisions in Angola’s governance lies in the decentralization of power and resources. Each province has its own government and administration, allowing for local decision-making and development...
Cultural or Historical Sites of Angola: Important Cultural Landmarks or Historical Sites In Angola
Angola, located on the western coast of Africa, is a country rich in cultural and historical sites. From ancient ruins to colonial architecture, Angola’s heritage tells the story of its diverse past. Preserving these sites is crucial for future generations to understand and appreciate the country’s history and cultural identity. Summary Angola has a rich cultural and historical heritage, with many sites of significance. Luanda, the capital city, has a fascinating history that reflects Angola’s colonial past. The Kongo Kingdom played a significant role in Angola’s history and is still celebrated today. The Great Zimbabwe ruins in Angola are shrouded in mystery and intrigue. The legacy of Portuguese colonialism is still evident in Angola’s culture and architecture. The Rich History of Angola’s Capital City, Luanda Luanda, the capital city of Angola, has a fascinating history that dates back to pre-colonial times. Originally inhabited by the Ambundu people, Luanda became an important trading post for the Portuguese in the 16th century. Over the centuries, it grew into a bustling city with a mix of African, European, and Brazilian influences. One of the key historical sites in Luanda is Fortaleza de São Miguel, a fortress built by the Portuguese in the 16th century to protect their interests in the region. Today, it serves as a museum that showcases the city’s colonial past. Another important site is the National Museum of Slavery, which documents Angola’s role in the transatlantic slave trade and educates visitors about this dark chapter in history. The Significance of the Kongo Kingdom in Angola’s History The Kongo Kingdom played a significant role in shaping Angola’s history. Established in...
Climate Zones of Angola: Different Climate Regions Of Angola
Angola, located on the west coast of southern Africa, is a country known for its diverse geography and climate. The country is characterized by a wide range of climate zones, each with its own unique characteristics and ecosystems. From tropical savannas to coastal deserts, Angola’s climate zones offer a variety of landscapes and opportunities for both its people and its economy. Summary Angola has a diverse range of climate zones, including tropical savanna, semi-arid, subtropical highland, humid subtropical, and coastal desert. The tropical savanna region covers most of Angola and experiences a wet and dry season, with temperatures ranging from 20-30°C. The semi-arid region is located in the south and east of Angola and experiences hot and dry conditions, with temperatures reaching up to 40°C. The subtropical highland region has cooler temperatures due to its higher altitude, with temperatures ranging from 10-20°C. The humid subtropical region experiences high levels of rainfall and humidity, with temperatures ranging from 20-30°C. Factors influencing Angola’s climate zones include latitude, altitude, ocean currents, and prevailing winds. Angola’s climate zones have a significant impact on agriculture and the economy, with the tropical savanna region being the most suitable for farming. Climate change is affecting Angola’s climate zones, with increased temperatures and changes in rainfall patterns. Angola’s diverse climate zones are significant for the country’s biodiversity and provide opportunities for tourism and economic development. Tropical savanna climate region The tropical savanna climate region in Angola is characterized by hot temperatures and distinct wet and dry seasons. This climate zone covers a large portion of the country, particularly in the central and northern regions. Cities such as...
Terrain and Topography of Angola: mountains, valleys, and plains.
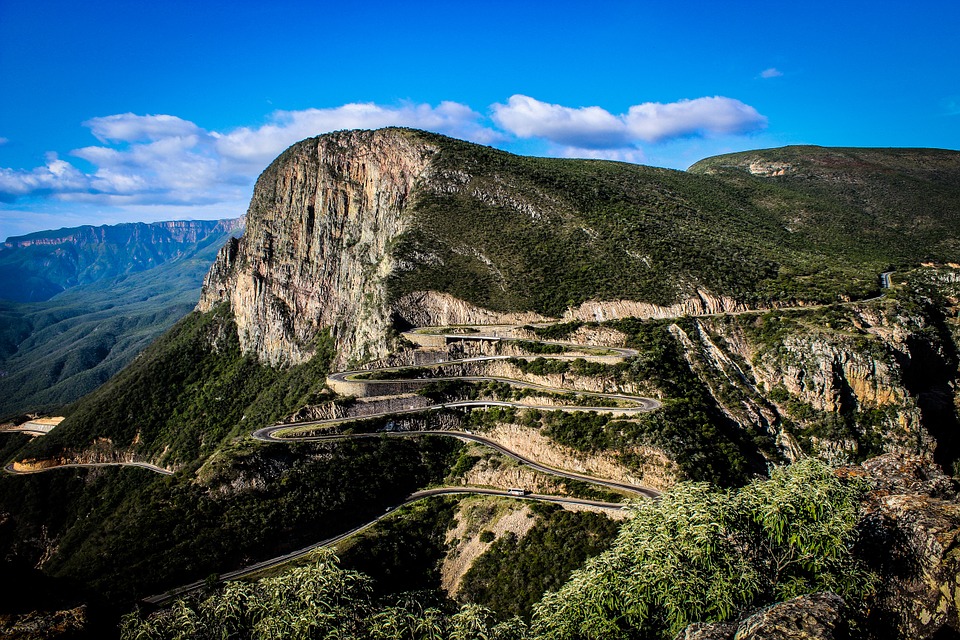
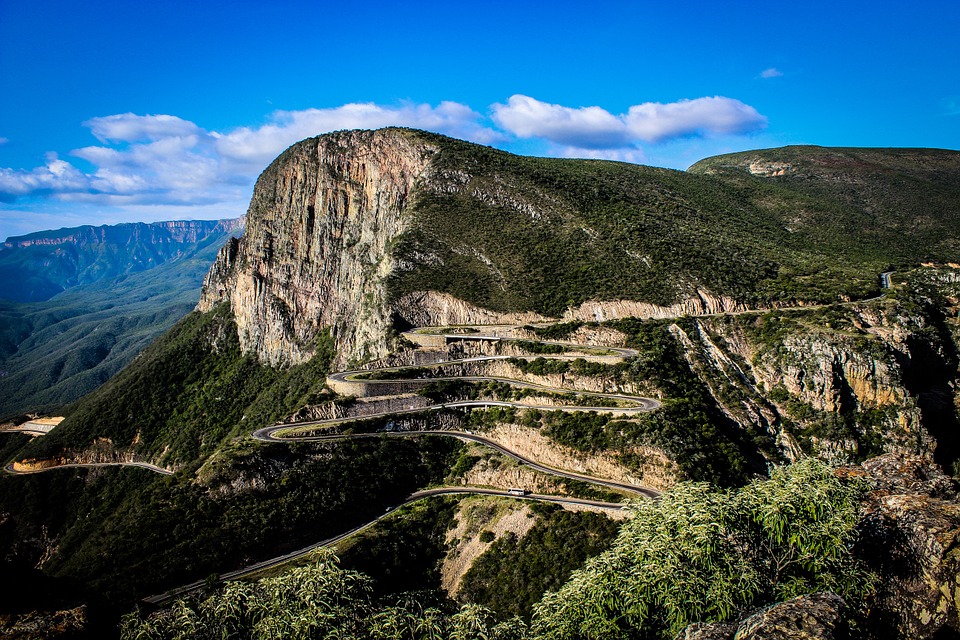
Angola, located on the western coast of Southern Africa, is a country known for its diverse and stunning terrain. From majestic mountains to vast plains, Angola’s topography offers a wealth of natural beauty and resources. Understanding Angola’s terrain and topography is crucial for various reasons, including agriculture, economy, and tourism. By exploring the different aspects of Angola’s geography, we can gain a deeper appreciation for the country’s natural wonders and the opportunities they present. Summary Angola’s terrain is diverse and varied, with mountains, valleys, plains, and unique geology. The majestic mountains of Angola offer stunning views and opportunities for exploration. The valleys of Angola are rich in biodiversity and offer unique opportunities for agriculture and tourism. The vast plains of Angola are home to a variety of wildlife and offer opportunities for ranching and agriculture. Angola’s unique geology, including diamonds and oil reserves, has played a significant role in the country’s economy. The Majestic Mountains of Angola Angola is home to several mountain ranges that add to the country’s breathtaking landscape. The most prominent mountain range is the Serra da Chela, located in the southwest region of Angola. This range stretches for approximately 200 kilometers and reaches elevations of up to 2,620 meters at its highest peak, Mount Moco. Mount Moco is not only the highest peak in Angola but also the highest in all of Southern Africa. Another notable mountain range in Angola is the Serra da Leba, famous for its stunning winding road that offers panoramic views of the surrounding valleys. The range reaches elevations of up to 1,845 meters at its highest point. These mountains have...
Population Density of Angola
Angola, located in Southern Africa, is a country with a diverse population and varying population density across its regions. Understanding population density is crucial for policymakers and stakeholders as it helps in planning and implementing effective policies and programs. Population density refers to the number of people living in a specific area, usually measured in terms of persons per square kilometer. By analyzing population density, we can gain insights into the distribution of resources, infrastructure needs, and social services required to meet the needs of the population. Summary Angola has a population density of 26 people per square kilometer. Angola’s population has grown rapidly since the 1950s due to improved healthcare and infrastructure. The majority of Angola’s population is concentrated in the northern and coastal regions. Urbanization has led to a significant increase in population density in Angola’s major cities. Angola’s high population density poses challenges for managing resources and providing basic services. Historical Overview of Angola’s Population Angola has a rich history that has influenced its population growth over the years. The country experienced significant population growth during the colonial period when it was under Portuguese rule. The Portuguese brought in large numbers of settlers and forced laborers from other African countries, resulting in an increase in the population. However, this growth was not evenly distributed across the country, with coastal areas experiencing higher population densities compared to the interior regions. Current Population Trends in Angola As of 2021, Angola has an estimated population of around 33 million people. The country has experienced steady population growth over the years, with an average annual growth rate of around 2%....
Exploring the Rich Culture and Natural Wonders of Angola: A Journey Through the Heart of Africa
Located on the west coast of Southern Africa, Angola is a country known for its rich cultural heritage, diverse landscapes, and warm and welcoming people. With a history that dates back thousands of years, Angola has a unique blend of African, Portuguese, and indigenous influences that can be seen in its art, music, cuisine, and architecture. From the bustling capital city of Luanda to the remote villages and stunning natural wonders, Angola offers a wealth of experiences for travelers seeking adventure, culture, and relaxation. Angola’s history is a complex tapestry of colonization, independence struggles, and post-war reconstruction. The country gained independence from Portugal in 1975 after a long and bloody war. Since then, Angola has made great strides in rebuilding its infrastructure and developing its economy. Today, it is one of the fastest-growing economies in Africa and has become an increasingly popular destination for tourists looking to explore its unique attractions. Key Takeaways Angola is a diverse and beautiful country with rich cultural heritage and natural wonders. The country’s national parks and wildlife reserves offer a unique opportunity to explore its wildlife and landscapes. Angola’s music and dance scene is vibrant and worth experiencing. The country’s cuisine and local delicacies are delicious and worth sampling. Angola’s friendly people offer a warm welcome to visitors. Discovering the Rich Cultural Heritage of Angola Angola is home to a diverse range of ethnic groups, each with their own unique traditions and customs. From the Ovimbundu in the central highlands to the Bakongo in the north and the Ovambo in the south, Angola’s cultural heritage is as diverse as its landscapes. Visitors to...